
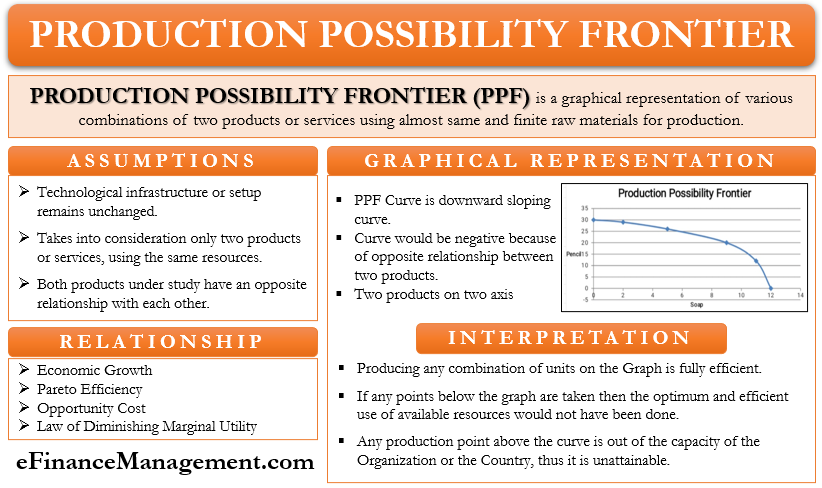
As the opportunity cost of producing 1 more good increases while society's aggregate desire for the good decreases, then there is a certain quantity of each individual good or service that provides the maximum satisfaction to society. Furthermore, as the supply of one good increases, the demand for the good decreases - in other words, society wants it less. But when production exceeds a certain amount, then the opportunity cost starts to increase. Because of economies of scale, opportunity costs at first decline when producing more goods. Allocative Efficiencyīecause the opportunity cost of producing more goods increases after a certain quantity, a point will be reached for which the cost of producing 1 more good is less than its benefit to society. This exemplifies the law of diminishing returns.

In our bread example, farmers would first use the best land to grow the grains necessary to produce bread, but if our simplified economy wanted to produce mostly bread, it must grow grains on less suitable land or in a less suitable climate. For example, if a factory is already operating near capacity, then to increase its output, it must hire more labor, train new workers, and utilize space that was devoted to other resources. But as the number and quantity of goods increases, then other factors of production, less efficient, must be used. Sacrificing the production of guns to make 1 more unit of bread is the opportunity cost of bread in our simplified economy, equal to the number of guns given up to make that unit of bread.Īs more resources are allocated to produce one good, the cost of an additional unit of the good increases after a certain point, because when only a few units of the good are produced, then the most suitable factors of production are used, lowering the cost of producing the good. Increasing Opportunity CostĮvery specific allocation of resources has an opportunity cost, which is what is given up to produce a specific good. Production outside of the curve is unattainable, and production below the curve is attainable but without using all resources, which violates the assumptions and reduces the aggregate wealth of society. Consider the production possibilities between bread and guns.Īny movement along the curve indicates the reallocation of resources from one good to the other, from guns to bread or vice versa.
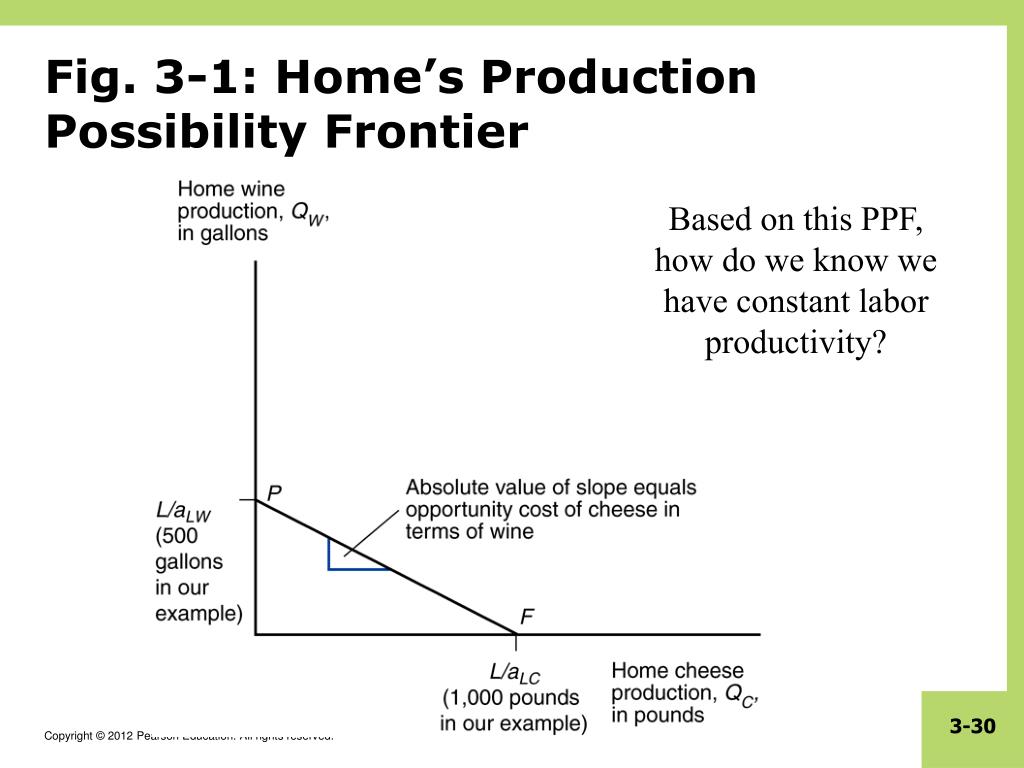
Thus, making these assumptions simplifies the analysis.
A production possibilities frontier shows full#
So if employment was less than full employment or productive efficiency was less than the maximum, then that introduces other production possibilities, such as increasing productive efficiency or increasing employment. The purpose of the assumptions is to show how the production possibilities of an economy changes with the allocation of its resources, so we must assume that nothing else changes - as economists like to say, ceteris paribus, meaning all other factors remaining the same.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
